Water Coming Up From Toilet and Shower Fixes & Prevention
Water coming up from the toilet and shower? This isn’t a normal plumbing situation. It could be a clogged drainpipe, a faulty trap, or even a pressure issue. We’ll explore the causes, from simple clogs to more complex plumbing problems, showing you how to pinpoint the source and get your plumbing working smoothly again. Let’s dive into the troubleshooting process and prevent future issues.
Understanding the different plumbing components involved is key to tackling this problem effectively. We’ll cover everything from identifying the root cause of the backup to fixing it and even how to prevent future backups. This guide provides a comprehensive look at the issues, solutions, and maintenance steps you can take.
Identifying the Source of the Issue

Source: waterheaterhub.com
Plumbing problems, especially those involving water backing up in toilets and showers, can stem from a variety of issues within the plumbing system. Pinpointing the exact cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair. Understanding the potential causes and their associated symptoms can significantly speed up the process of identifying the problem and getting your plumbing back to normal.
Potential Causes of Water Backup
Knowing what could be causing the water backup is the first step in fixing the problem. Different parts of the plumbing system can contribute to this issue. The following list of Artikels common culprits and the signs they often display.
- Clogged Drainpipes: Foreign objects, hair, soap scum, or other debris can accumulate in drainpipes, restricting water flow. This blockage often leads to slow draining in toilets and showers. You might hear a gurgling sound as the water struggles to pass through the blockage. If the clog is severe, water may overflow from the affected fixtures.
- Faulty Drain Traps: A drain trap’s primary function is to prevent sewer gases from entering the house. A damaged or improperly installed trap can allow water to back up. This often manifests as water backing up in the toilet or shower, with the level rising in the affected fixture. You might hear a gurgling or bubbling sound, especially when running water elsewhere in the house.
- Clogged or Blocked Vents: Vents in the plumbing system are crucial for maintaining proper air pressure. If a vent becomes blocked, it can affect the flow of water, leading to clogs in drains and traps. Signs of a blocked vent include slow draining in multiple fixtures, gurgling sounds, and even occasional overflowing. In some cases, this is a less direct problem, causing other issues to become apparent.
- Low Water Pressure: Sometimes, low water pressure in the main water supply can contribute to water backing up in toilets and showers. The water simply isn’t forceful enough to push the water through the drain effectively, leading to a backup in the affected fixtures. This can often be a symptom of issues beyond the local plumbing.
- Frozen Pipes: In colder climates, frozen pipes can disrupt water flow, leading to water backing up in the affected fixtures. The ice buildup prevents the water from flowing through the pipe correctly. This is more likely to affect pipes outside of the home but can impact fixtures if the issue isn’t contained.
Symptom Comparison
This table summarizes the potential causes and their corresponding symptoms, helping you quickly identify the problem:
| Cause | Symptom | Possible Location |
|---|---|---|
| Clogged Drainpipe | Slow draining, gurgling sounds, occasional overflowing | Toilet/Shower Drain |
| Faulty Drain Trap | Water backing up in the fixture, gurgling/bubbling sounds, especially when running water elsewhere | Shower/Sink/Toilet drain trap |
| Clogged or Blocked Vents | Slow draining in multiple fixtures, gurgling sounds, overflowing | Throughout the plumbing system, often above or near the affected fixture |
| Low Water Pressure | Slow draining, water backing up in the fixture | Main water supply or beyond the local plumbing system |
| Frozen Pipes | Water backing up in the fixture, lack of water flow | Frozen sections of the pipe, often outside the home |
Investigating Plumbing System Components

Source: waterheaterhub.com
Now that we’ve identified the general area of the problem, it’s time to get hands-on and inspect the specific plumbing components involved. This section details a methodical approach to examining the toilet and shower plumbing, equipping you with the necessary tools and knowledge to pinpoint the source of the water issue.
This thorough inspection will guide you toward the root cause, whether it’s a simple clog or a more complex problem within the drain lines or fittings. Knowing how to systematically inspect these components is crucial for efficient troubleshooting and effective repairs.
Toilet Plumbing Inspection Procedure
This procedure Artikels a step-by-step approach to inspect the toilet’s plumbing, enabling you to identify potential issues.
- Isolate the Water Supply: Turn off the water supply valve to the toilet. This is crucial for safety and prevents further water damage while working.
- Inspect the Tank: Visually examine the tank for any visible leaks, cracks, or damage to the overflow tube. Look for corrosion or rust, which can indicate a potential leak point.
- Check the Flush Mechanism: Examine the flapper or ball valve for proper seal and function. A leaky flapper or a malfunctioning chain can cause constant water flow into the bowl.
- Inspect the Bowl: Check the bowl for any visible cracks, damage, or clogs. Observe the water level in the bowl. An unusually low water level might suggest a leak in the bowl or a slow leak elsewhere in the system.
- Check the Drain Line: Carefully inspect the drain line near the base of the toilet for signs of clogs, cracks, or leaks. Check the connection between the toilet and the drain pipe.
Shower Plumbing Inspection Procedure
This procedure Artikels a systematic inspection of the shower plumbing, helping to pinpoint the source of water issues.
- Isolate the Water Supply: Turn off the water supply valve to the shower. This is essential for safety and prevents water damage while working.
- Inspect the Showerhead and Faucet: Check for leaks, loose connections, or clogs in the showerhead and faucet. Look for any damage to the shower arm or valves.
- Examine the Drain Line: Inspect the drain line connected to the shower for clogs, cracks, or leaks. Check the connection between the shower drain and the main drain line.
- Inspect the Shower Valve(s): Carefully examine the shower valve(s) for leaks, damage, or clogs. A dripping shower valve is a common sign of a problem.
- Check for Leaks at Connections: Inspect all connections, including the shower pipe, drain, and any fittings, for leaks or corrosion. Look for signs of moisture or water stains around the connections.
Tools and Equipment Needed
A well-equipped toolbox is essential for a comprehensive plumbing inspection.
- Screwdrivers: Phillips and flathead screwdrivers are essential for disassembling parts.
- Pliers: Needle-nose pliers are useful for handling small parts and tightening connections.
- Adjustable Wrench: For loosening and tightening nuts and bolts.
- Flashlight or Lamp: A good light source is crucial for inspecting hard-to-reach areas.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from sharp edges and potential contaminants.
Inspection Checklist for Drain Lines and Fittings
This checklist guides you in examining the drain lines and fittings for any potential problems.
- Leaks: Look for water stains, dampness, or drips around pipes, fittings, and connections.
- Clogs: Check for any obstructions or blockages in the drain lines.
- Corrosion: Inspect for rust, pitting, or other signs of corrosion on metal pipes or fittings. Severe corrosion can lead to leaks.
- Loose Connections: Verify that all pipe connections are secure and not vibrating or loose.
- Damage: Look for cracks, breaks, or any visible signs of damage to pipes and fittings.
Visual Characteristics of Damaged Components
Recognizing the signs of damaged components is critical for identifying the source of the problem.
- Leaks: Drips, water stains, or pools of water around pipes or fittings.
- Clogs: Slow or sluggish draining, unpleasant odors, or water backing up.
- Corrosion: Rust, pitting, or discoloration on metal pipes or fittings.
- Loose Connections: Wiggling or vibrating pipes or fittings.
- Damage: Cracks, breaks, or missing pieces in pipes or fittings.
Potential Troubleshooting Solutions

Source: plumbingemergencyrescue.com
Now that we’ve identified the source of the water issues, it’s time to fix them. This section applies various approaches, from simple fixes to more involved plumbing repairs. Understanding the specific problem is key to choosing the right solution and avoiding unnecessary work.
Simple Fixes for Minor Leaks
These solutions often address clogs or minor leaks that are easy to address without extensive tools or expertise.
- Inspect and Clean the Toilet’s Flapper/Overflow Tube: A flapper that’s worn or misaligned, or a clogged overflow tube can cause constant dripping or slow draining. A simple check and replacement with a new flapper or unclogging the tube might resolve the issue. This is often the first place to start with toilet problems.
- Check and Adjust the Showerhead and Faucet: Inspect the showerhead for debris or clogs, and adjust the faucet’s aerator to ensure proper water flow. A clogged showerhead will produce a sputtering effect, or reduced water pressure. Likewise, a faucet aerator that’s obstructed or worn can also lead to leaks or inconsistent water pressure.
- Verify the Drain Trap: A drain trap (often under a sink or near a drain) can accumulate debris. Inspecting it and clearing any obstructions can resolve issues with slow drainage. A clogged drain trap prevents proper water from flowing away, which can cause backflow into your toilet or shower.
Addressing Clogged Pipes
Sometimes, clogs in pipes can lead to water backing up into the toilet or shower.
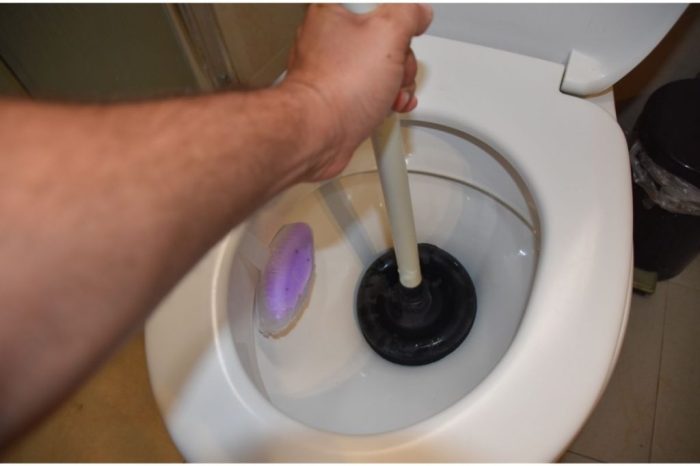
- Using a Plunger: A plunger can effectively clear blockages in toilets or sinks, especially if the blockage is not severe. The plunger creates suction to dislodge the clog and allow water to drain properly. Proper plunger technique is crucial for effectiveness.
- Employing a Drain Snake/Plumbing Auger: A drain snake helps reach clogs further down the drain line. Insert the snake into the drain, rotating it to break up the clog. This is more effective than a plunger for stubborn clogs in drains or pipes, and less damaging to the pipe if done carefully.
- Consider a Chemical Drain Cleaner: Chemical drain cleaners can help break down organic matter that might be causing a clog. Use with caution, as these chemicals can damage pipes if used excessively or improperly. Follow the product instructions carefully. Note: Using these solutions too frequently or excessively may damage your pipes.
More Complex Plumbing Issues
These repairs might require professional assistance due to the complexity or the need for specialized tools.
- Replacing Pipes: If pipes are cracked, corroded, or have suffered significant damage, they might need to be replaced. This is often a more complex and time-consuming job. Replacing pipes requires specialized tools and knowledge of plumbing codes.
- Addressing Water Pressure Issues: If you have inconsistent or low water pressure, there may be a problem with the water supply line or the main water valve. A plumber can diagnose and resolve these issues effectively. This is often a job for a professional plumber due to the potential complexity of the plumbing system and the potential damage to your pipes or water system.
Preventing Future Issues

Source: newflowplumbing.com
Keeping your plumbing system in tip-top shape isn’t just about fixing problems when they arise; it’s about proactive maintenance to avoid future headaches. By understanding the common causes of clogs and implementing preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of costly repairs and frustrating backups. Regular maintenance is key to long-term plumbing health.
Proper preventative maintenance is crucial for maintaining a functional and reliable plumbing system. This proactive approach ensures smooth water flow and prevents the buildup of debris that can lead to blockages. By addressing potential issues early, you can avoid the inconvenience and expense of extensive repairs.
Toilet Maintenance
Regular toilet maintenance is essential for preventing clogs and ensuring proper functionality. Cleaning the toilet regularly, along with inspecting the drain line, helps maintain a clear and efficient system. This involves removing any foreign objects that may find their way into the drain line. A clogged toilet can quickly turn into a major plumbing problem.
Shower Drain Maintenance
Shower drains, just like toilet drains, are susceptible to clogs. Regular cleaning of the drain traps, combined with proper disposal habits, can help prevent clogs and maintain smooth water drainage. This is especially important for showers with multiple drain lines, as clogs can occur more quickly.
Preventative Maintenance Schedule
This table Articulates a recommended preventative maintenance schedule for toilets and showers. Adhering to these guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of future issues.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect drain lines | Monthly |
| Check for clogs | Weekly |
| Clean drain traps | Quarterly |
Proper Disposal Practices
Proper disposal practices play a vital role in preventing clogs. Understanding what items should and shouldn’t be flushed down the toilet or drain is essential for maintaining a healthy plumbing system. Improper disposal habits are often the root cause of plumbing issues.
Items to Avoid Flushing, Water coming up from the toilet, and shower
Avoid flushing these items down the toilet or drain to prevent clogs:
- Feminine hygiene products
- Wipes (including baby wipes and facial tissues)
- Cotton swabs
- Dental floss
- Food scraps
- Grease or oil
- Paper towels
- Sanitary napkins
- Non-flushable cleaning products
- Household chemicals
- Prescription drugs
Flushing these items can lead to clogs in the pipes and cause backups, resulting in costly repairs and inconvenience. Proper disposal of these items is key to maintaining a healthy and efficient plumbing system.
Visual Representation of Common Issues

Source: newflowplumbing.com
Plumbing problems can be tricky to diagnose, especially when you’re dealing with backups. Seeing how water flows through the system, and visualizing potential blockages, can be a big help. Understanding the typical plumbing layout in your house and the flow path of water is key to finding the source of the issue.
Toilet Backup Scenario
Imagine a typical house with a main water supply feeding various fixtures. The toilet, sink, and shower are connected to a drain line that runs to a main sewer line. A crucial part of this system is the trap, a U-shaped pipe that prevents sewer gases from entering the house. This scenario involves a blockage in the drain line, specifically affecting the toilet.
Plumbing System Description
The plumbing system consists of:
- A main water supply line brings water into the house.
- Individual supply lines feed water to each fixture (toilet, shower, sink).
- Drain lines connect each fixture to a main drain line that leads to the sewer.
- A P-trap under the toilet prevents sewer gases from entering the house.
- A main drain line carrying wastewater from multiple fixtures to the sewer.
In this scenario, a buildup of debris, like paper, soap scum, or even a slow leak in a pipe, has created a blockage in the drain line near the toilet.
Water Backing Up From a Toilet
Visualizing the water backing up from the toilet is like seeing a dam forming in the drain line. The blockage prevents water from flowing through the drain line, causing it to overflow and push back into the toilet bowl. The water level in the toilet rises significantly, potentially spilling over the rim and onto the floor. Imagine a gradually filling sink, only instead of the sink, it’s the toilet bowl. This overflow is a clear sign that there’s a blockage further down the drain line.
Water Flow During Blockage
Normally, water flows downhill from the fixtures, through the drain line, and eventually into the sewer. A blockage interrupts this flow. The water behind the blockage has nowhere to go, causing it to rise in the pipes connected to the blockage. In the case of the toilet, the blockage causes water to back up into the toilet bowl. This overflow is a crucial visual clue that there’s a blockage somewhere in the drain line.
Understanding Water Pressure and Flow: Water Coming Up From Toilet And Shower

Source: home dude.co
Water pressure and flow are fundamental to the proper operation of your toilet and shower. They dictate how quickly and efficiently water is delivered and drained, impacting everything from the strength of the spray to the speed of flushing. Understanding the relationship between these two elements is crucial for diagnosing and preventing plumbing problems.
Proper water pressure ensures a strong and consistent water flow, which is necessary for effective cleaning and efficient flushing. Conversely, inadequate water pressure can lead to weak streams, sluggish flushing, and potentially even damage to the plumbing system.
Role of Water Pressure in Toilet and Shower Operation
Water pressure, measured in PSI (pounds per square inch), directly influences the force and velocity of water delivered to your toilet and shower. Higher pressure results in a stronger spray and faster flushing. Conversely, lower pressure can lead to a weak stream, a slow flush, and a less effective cleaning experience. A consistently strong pressure ensures reliable flushing and thorough cleaning in your shower.
Importance of Proper Water Flow and its Impact on the Drainage System
Proper water flow is essential for efficient drainage. Water that flows too slowly or unevenly can cause clogs, backups, and potentially damage to your plumbing system. Too rapid a flow can sometimes lead to the same problems, or, in certain situations, cause fixtures to sputter or surge. A balanced flow is vital for maintaining a smooth and efficient drainage system.
Water Pressure and Drainage Relationship

Diagram Description: This diagram shows a simplified plumbing system. A water source (e.g., a city water main) is connected to a pressure regulator, then to pipes that deliver water to the toilet and shower. The diagram highlights the pipes carrying water to the fixtures and the drain lines. Arrows indicate the direction of water flow. The diagram shows how water pressure impacts the speed of water through the pipes and how this, in turn, influences the drainage system. A crucial aspect illustrated is the relationship between the water pressure and the speed at which water exits the fixtures and drains into the plumbing system. A proper balance between the pressure and flow is critical for efficient drainage, avoiding clogs or slowdowns.
Effects of Fluctuating Water Pressure on Plumbing Systems
Fluctuating water pressure can cause several problems in your plumbing system. Sudden pressure surges can damage pipes, valves, and fixtures. Conversely, prolonged low pressure can lead to slow flushing, reduced water flow, and potential clogs. Real-world examples include instances where a pressure fluctuation is caused by nearby construction or an event that leads to a disruption in the water supply’s pressure regulation. Understanding how these fluctuations affect your system is critical for maintenance and repair.
Conclusive Thoughts

Source: premierplumbingandleakdetection.com
So, there you have it—a complete guide to dealing with water backing up from your toilet and shower. We’ve covered the common causes, how to investigate the problem, potential fixes, and how to maintain your plumbing to avoid future issues. By following the steps in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to handle this common plumbing problem and keep your bathroom functioning perfectly. Remember, prevention is key, and a little proactive maintenance can save you a lot of trouble and money down the line.